
Unraveling Blockchain Transactions
Blockchain, the technology underpinning cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has garnered significant attention for its potential to revolutionize industries from finance to healthcare. At its core, a blockchain facilitates secure digital transactions, a concept many find elusive. Let’s demystify blockchain transactions and understand how they operate.
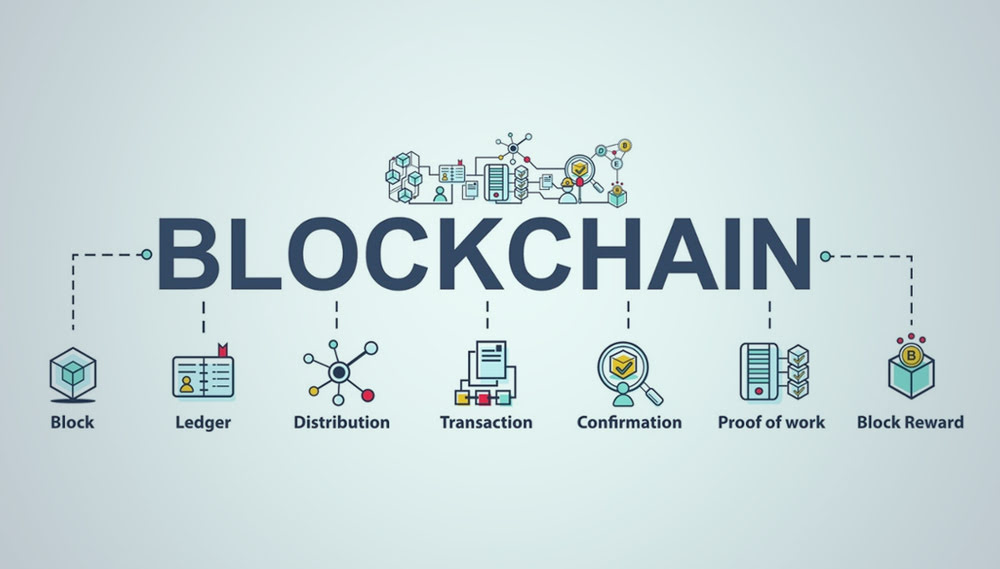
How the Blockchain is Structured and Works
Blockchain can be visualized as a digital ledger, but instead of being stored in one location, it’s distributed across numerous computers worldwide. Every transaction made is stored in a ‘block’. Once this block is full, a new block is created, forming a ‘chain’ of blocks – hence, the name blockchain.
For instance, consider the bet-nero.net online casino, which might use blockchain technology for transactions. When a player makes a bet or withdraws winnings, this action is recorded as a transaction, encrypted, and added to a block.
Types of Blockchains
- Public Blockchains: Open to anyone, participants can join and perform transactions. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples.
- Private Blockchains: Access is restricted. They’re typically used by businesses and enterprises for internal processes
- Consortium Blockchains: Controlled by a group rather than a single entity. Multiple organizations might manage a node.
What are Bitcoin Transactions and How Are They Carried Out?
A Bitcoin transaction involves transferring ownership of a certain amount of Bitcoin from one address to another. Key components include the input (source transaction of the Bitcoin), the amount to transfer, and the output (recipient’s address)
For a transaction to be executed, the sender must provide a digital signature using their private key. Once signed, it’s broadcasted to the network for verification. Miners then validate the transaction by solving complex mathematical problems.
How to Find and Track a Transaction
Every transaction on a blockchain has a unique ID. Using this ID on blockchain explorers (like BlockExplorer for Bitcoin), one can track the transaction’s details, including its status, timestamp, and included block.
What is a Transaction Fee?
Due to the decentralized nature of blockchains, there’s no central authority processing transactions. Instead, miners do this work and, in return, require a fee. This transaction fee acts as an incentive for miners to include the transaction in a block. Fees can vary based on network congestion and transaction size.
What is Transaction Confirmation?
Once a transaction is added to a block, it receives its first confirmation. More confirmations are received as more blocks are added. Each confirmation decreases the risk of a transaction being reversed. For Bitcoin, a common standard is to wait for six confirmations to consider a transaction irreversible.
Conclusion
Blockchain transactions, with their decentralized and transparent nature, offer a groundbreaking approach to digital transfers. While the underlying mechanics might seem intricate, understanding the basics, as detailed above, demystifies the complexities, allowing even novices to navigate the blockchain world with confidence.



